The electric bike motor is an ingenious component that turns a traditional bicycle into a power-assisted vehicle.
It serves as the centerpiece of any e-bike, responsible for providing the extra boost that elevates cycling from a physical challenge to an effortless and enjoyable experience. By reducing the effort needed to pedal, an e-bike motor allows riders to conquer steep hills, endure long-distance rides, and navigate difficult terrains with ease.
Whether you’re commuting to work or enjoying a weekend ride, an e-bike motor transforms your cycling experience into one of convenience and comfort.
Let’s take a closer look at the fascinating world of electric bike motors, their types, functionality, and how they can enrich your cycling journey.

Understanding the Types of Electric Bike Motors
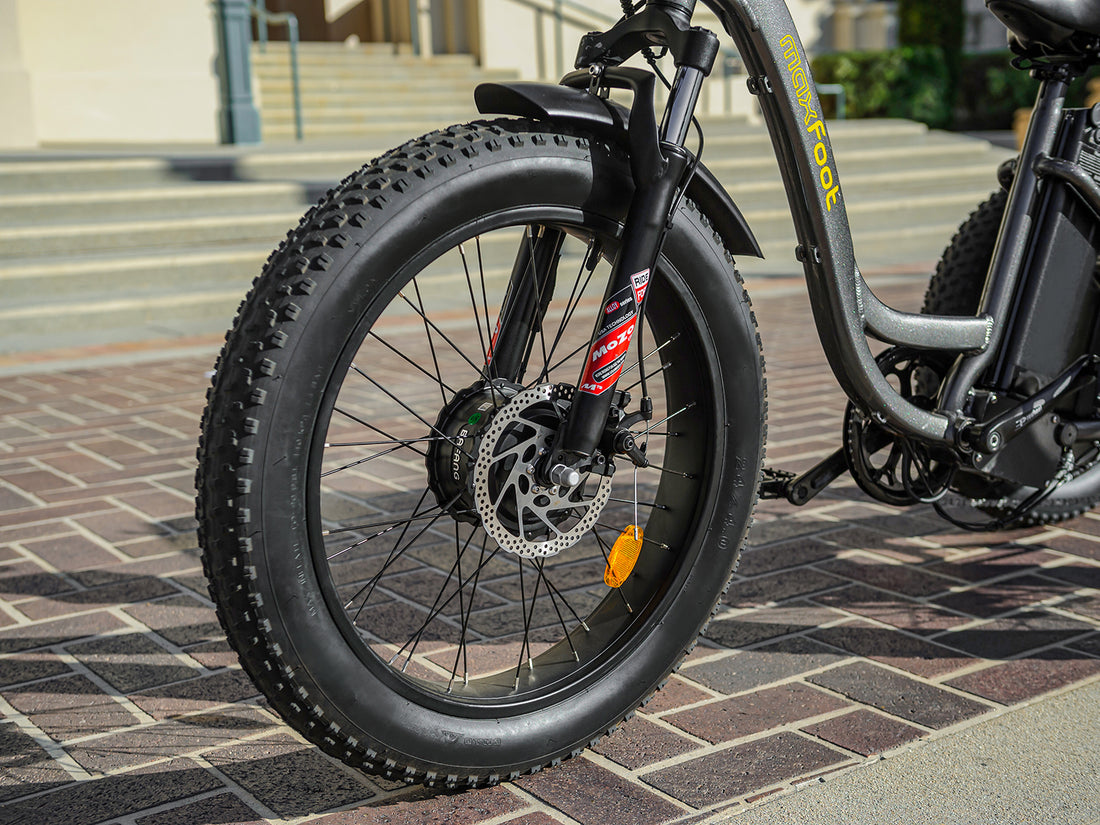
Electric bike or e trike motors are typically integrated into one of three areas: the front hub, rear hub, or central crankshaft. These motors fall into two primary categories: hub motors and mid-drive motors.
Let’s take a closer look:
1. Hub Motors
Hub motors are located either in the front or rear wheel hub. Each placement brings two different categories, such as front hub and rear hub motor, catering to different rider preferences and terrains.
Front Hub Motors:
Mounted in the front wheel hub, these motors provide a pulling sensation, effectively creating an all-wheel-drive system when combined with pedaling. This setup is ideal for casual riders navigating flat terrains or those seeking an affordable e-bike solution for commuting or leisure rides.
- Excellent for sand and snow due to added traction.
- Easy to install and remove since they don’t share space with the bike's gear system.
- Balanced weight distribution when paired with a centrally or rear-mounted battery.
- Minimal maintenance requirements.
- Budget-friendly option.
- Less powerful than rear hub motors.
- Can affect handling, particularly on loose terrain or during high-speed cornering.
Rear Hub Motors:
Rear hub motors, housed in the rear wheel, deliver a pushing sensation that feels natural, closely mimicking the motion of a traditional drivetrain. These motors are versatile and suited for casual commutes, hilly terrains, or riders seeking a balance of power and control.
- Provides a natural riding experience with its pushing motion.
- Generally more powerful, ideal for climbing hills.
- Minimal impact on handling, offering a responsive ride.
- Power directed through the rear wheel ensures minimal wheel spin.
- Works well with throttle functions for quick acceleration.
- May require a sturdier frame to manage torque demands.
- Potential for wheel slip on loose surfaces if not handled properly.
2. Mid-Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors are mounted directly at the crankshaft and transfer power through the bike's drivetrain, leveraging the gear system for optimal performance. This placement provides balanced weight distribution between the front and rear, enhancing stability and maneuverability. Mid-drive motors are particularly well-suited for riders tackling hilly or varied terrains, offering superior torque and a natural riding feel.

- Exceptional torque for climbing and accelerating.
- Balanced weight distribution enhances handling and control.
- Efficient use of battery power.
- Supports a wide range of assistance levels for nuanced riding experiences.
- Often provides the longest range of travel among e-bike or even e trike motors.
- Requires more frequent maintenance due to its drivetrain integration.
- Higher upfront cost compared to hub motors.
Motor Power and Wattage
Electric bike motor power is typically measured in watts (W). Wattage indicates the amount of energy the motor can handle and, consequently, the amount of assistance it can provide to the rider. In simple terms, the higher the wattage, the more powerful the motor.
However, it's important to note that motor power isn’t the sole factor affecting performance. Torque, battery capacity, and motor type also contribute to the ride quality. Together, these elements create a well-rounded riding experience that suits different needs and terrains.
Common Motor Wattage Ratings
- 250W: A 250W motor is lightweight, efficient, and meets most legal e-bike or e trike regulations globally. It provides sufficient power for commuting, city riding, and flat terrains.
- 500W: A middle-ground option, offering a good balance between power and efficiency. 500W motors are versatile and suitable for riders who need more torque and speed without sacrificing battery life.
- 750W and above: These motors deliver substantial torque and top speed, making them ideal for heavy-duty use, off-road adventures, or cargo bikes. These motors deliver significant power but consume more battery.
How Does Motor Power Affect the Ride?
The motor power of an e-bike directly influences several key aspects of its performance. Let’s explore the main factors:
- Speed: Generally, a motor with higher wattage allows for faster acceleration and higher top speeds. For example, a 250W motor might cap out at 15-20 mph, while a 750W motor could reach speeds up to 28 mph or more.
- Torque: Torque refers to the rotational force generated by the motor and is particularly important for hill climbing and carrying heavy loads. Motors with higher wattage usually deliver more torque, making them better suited for challenging terrains. On the other side, mid-drive motors often excel in torque delivery compared to hub motors.
- Battery Consumption: More powerful motors require more energy, which can reduce your bike's overall range. Riders should weigh their need for power against battery efficiency. A 250W motor paired with a high-capacity battery may offer a longer range than a 750W motor with the same battery size.

Motor Control and Assistance Levels
Electric bike motor control refers to the technology that determines how the motor operates based on rider input. It includes features like pedal assistance, throttle mechanisms, and customizable settings to suit various riding conditions.
With advancements in motor control systems, you can now enjoy smooth, intuitive, and efficient power delivery.
Pedal-Assist System (PAS)
Pedal-assist is the most common mode, where the motor activates only when you pedal. You can adjust the level of assistance, often ranging from eco-mode (minimal help) to turbo-mode (maximum power). The amount of "help" the system provides depends directly on the effort you put in through pedaling. The harder you pedal, the more assistance the motor delivers, creating a seamless and intuitive riding experience.
Benefits of PAS:
- Provides a natural and smooth cycling experience.
- Extends battery life by engaging the motor only when needed
- Encourages physical activity while providing relief when necessary
Throttle Control
Throttle control is another popular motor control feature on e-bikes, allowing riders to activate the motor without pedaling. Operated via a handlebar-mounted lever, grip, or button, the throttle delivers instant power, much like a scooter or motorcycle.
Benefits of Throttle Control:
- Convenient for quick starts or steep climbs
- Beginner-friendly and ideal for riders with limited physical strength
- Perfect for riders who need a break from pedaling or for those with limited physical strength.
Maintenance and Care Tips for E-Bike Motors
Maintaining your e-bike motor is crucial for ensuring long-lasting performance and avoiding costly repairs. While e-bike motors are generally low-maintenance, a few simple practices can go a long way.
- Regularly clean the motor area with a damp cloth, avoiding direct water exposure.
- Check for loose wires, connectors, or screws.
- For mid-drive motors, the motor directly engages the drivetrain. Regularly clean and lubricate the chain, sprockets, and derailleur to minimize wear caused by the motor's torque.
- Grinding, clicking, or buzzing noises can indicate internal issues. Address them promptly to prevent further damage.
- Avoid overworking the motor, especially on steep hills or long rides. Continuous overheating can lead to internal component failure.
- Even with routine care, schedule professional servicing annually or after heavy use. Trained technicians can inspect the motor and ensure all components are in good working order.
Conclusion
Electric bike motors are the driving force behind the growing popularity of e-bikes, offering unmatched convenience, efficiency, and versatility. Whether you're navigating city streets or exploring mountain trails, the right motor can transform your ride.
By understanding the types, power levels, and maintenance needs of e-bike motors, you can make an informed decision that suits your lifestyle and ensures years of smooth cycling.
So gear up, choose wisely, and let the power of an e-bike motor elevate your adventures.